By: Henry VanBuskirk, CFP®, Wealth Manager
(This is part 4 of a four-part estate planning series)
In the previous posting, we discussed how Mark Zuckerberg of Meta Platforms, Inc. had the same strategies available, that you have available in order to reduce or possibly eliminate your estate tax bill. In this final part of the estate planning series, we would like to review how gifting assets from your estate can be beneficial to your estate tax bill. If you have concerns regarding how these strategies could affect certain estate and gift planning transactions in which you intend to engage or have previously engaged, please contact your tax advisor and estate planning attorney to further discuss your estate and gift planning inquiries. Our firm is happy to work with you and your estate planning attorney on your unique situation and we can work together to help you achieve your estate planning goals.
During my CFP® studies, one of my professors quipped, “Some people are charitable by choice, but some people get to a certain level of net worth and are charitable by necessity.” This means that even though some people aren’t charitably inclined, it may be best for their bottom line to be charitable for their own sake and/or their heir’s sake.
The Charitable Remainder Trust (CRT) and the Charitable Lead Trust (CLAT)
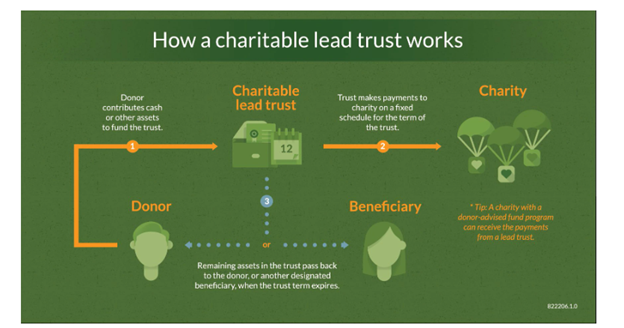
I’ve lumped these two strategies together because they generally both gift assets to charity and get assets out of the estate, but one pays the charity in a lump sum and the other pays an annual income stream to the charity over a stated number of years. When a Charitable Remainder Trust (CRT) is funded, income gets paid to the beneficiary(ies) at least annually for a set number of years and the charity gets the remainder. The Charitable Lead Annuity Trust (CLAT) (sometimes referred to as just a Charitable Lead Trust) is structured where income gets paid to the charity over a stated number of years and afterward, the beneficiary(ies) gets the remainder. Both trusts are irrevocable and serve the purpose of lowering your taxable estate. The CRT allows for an immediate charitable deduction when you fund the trust, while the CLAT allows the estate to take a charitable deduction for the value of the interest paid to charity.
Here are some graphical examples of how a Charitable Remainder Trust and Charitable Lead Annuity Trust work:
Charitable Remainder Trust (CRT):
Charitable Lead Annuity Trust (CLAT)
Superfunding 529 Plans
The 529 plan is an investment account typically used for college planning that allows for tax-free growth and possible tax-free distributions if those distributions are made to pay for qualified educational expenses. One strategy that is available to you is using the annual gift tax exemption of $16,000 per person per beneficiary since (as we discussed in part 1 of this series) this is typically the maximum that you can gift without triggering the gift tax and having your gift tax exclusion reduced. However, we can do one better. You can “superfund” a 529 plan by making five years’ worth of gifts in one year. Therefore, we can gift $80,000 per person per beneficiary (or if you are a married couple, you can use gift splitting and instead gift $160,000 per beneficiary) all without triggering gift tax and while getting that $160,000 out of the estate. Notice that the definition states: “per beneficiary”. The catch is that you need to live at least 5 years after the gift is made for it to have successfully left your estate. After the first five years are completed, you can do it again if you wish. If one of the 529 plan beneficiaries decides not to go to college, you can always change the beneficiary at any time, or even make a once per year rollover of 529 plan assets to another 529 plan beneficiary’s account.
529 Plan Superfunding Example: Say you have six grandchildren, and you are benevolent Grandma and Grandpa. You want to superfund their 529 plans, so you then make a gift of $160,000 to each of the six grandchildren to their 529 plan accounts (for a total of $960,000). You wait 5 years and do it again, but unfortunately, passed away 2 years later. The first $960,000 that you gifted will be out of your estate. But the second time you tried to superfund their 529 plans for the second $960,000, it will be counted in your gross estate. In this example, there was still $1,920,000 contributed to the six grandchildren’s 529 plans and $960,000 left in your gross estate – all without triggering any gift tax.
In summary, there are many different estate planning strategies that can help reduce your overall income tax burden. If you would like to revisit any of our prior posts in this estate planning series here are the articles for easy reference:
- What is the Estate and Gift Tax
- Getting Assets out of the Estate
- Getting Future Growth out of the Estate
Furthermore, earlier this year we posted a white paper, “2022 Estate and Gift Tax Planning”, that discussed making gifts to children and grandchildren during 2022 while incurring little or no gift tax.
The bottom line is we are happy and willing to work with you and your estate planning attorney on your unique estate planning goals.
Disclosure: BFSG does not make any representations or warranties as to the accuracy, timeliness, suitability, completeness, or relevance of any information prepared by any unaffiliated third party, whether linked to BFSG’s website or blog or incorporated herein and takes no responsibility for any such content. All such information is provided solely for convenience purposes only and all users thereof should be guided accordingly. Please remember that different types of investments involve varying degrees of risk, and there can be no assurance that the future performance of any specific investment or investment strategy (including those undertaken or recommended by Company), will be profitable or equal any historical performance level(s). Please see important disclosure information here.